In recent years, the DASH diet has gained significant recognition for its role in promoting health and preventing chronic diseases. Developed to combat high blood pressure, the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is not only effective for managing hypertension but also offers a comprehensive approach to overall wellness. This article delves into the intricacies of DASH diet plans, providing detailed insights into its benefits, principles, and practical implementation.
Understanding the DASH Diet


What is the DASH Diet?
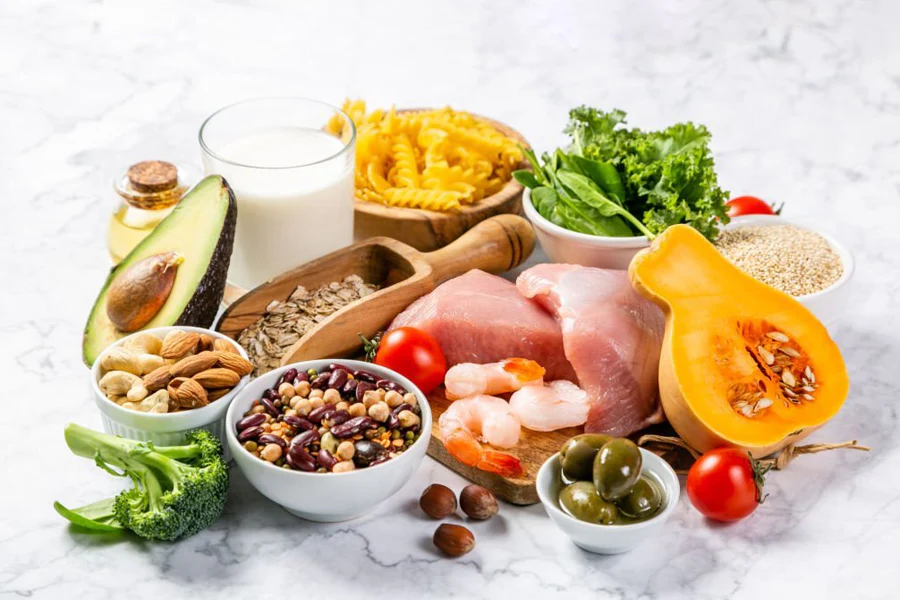
The DASH diet is a scientifically-backed nutritional plan designed to help reduce blood pressure and improve heart health. It emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products while limiting the intake of sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars. The diet’s primary focus is on nutrient-dense foods that are rich in potassium, calcium, magnesium, and fiber—nutrients known to help lower blood pressure.
Health Benefits of the DASH Diet
The DASH diet is renowned for its multiple health benefits, including:
- Lower Blood Pressure: By reducing sodium intake and incorporating potassium-rich foods, the DASH diet effectively lowers both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
- Improved Heart Health: The emphasis on heart-healthy foods helps reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular risk.
- Weight Management: The diet’s balanced approach promotes sustainable weight loss and maintenance.
- Reduced Risk of Diabetes: High-fiber foods and a focus on whole grains help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Enhanced Overall Nutrition: By encouraging a variety of nutrient-dense foods, the DASH diet ensures comprehensive nutritional intake.
Core Principles of the DASH Diet

Focus on Whole Foods
The DASH diet prioritizes whole, unprocessed foods. This means fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains like brown rice and quinoa, lean meats, fish, poultry, and nuts and seeds. These foods provide essential nutrients without excessive calories or unhealthy additives.
Sodium Reduction
A key component of the DASH diet is limiting sodium intake to help manage blood pressure. The standard DASH diet recommends no more than 2,300 mg of sodium per day, while the lower-sodium version suggests reducing this further to 1,500 mg per day.
Balanced Nutrient Intake
The diet emphasizes a balance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). It encourages the intake of foods high in potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which play crucial roles in blood pressure regulation.
Portion Control
Understanding and controlling portion sizes is vital in the DASH diet. This helps prevent overeating and ensures that caloric intake aligns with individual energy needs.
Implementing the DASH Diet: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Assess Your Current Diet
Start by evaluating your current eating habits. Identify areas where you can reduce sodium and increase the intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Keeping a food diary can be an effective way to track your progress and make necessary adjustments.
Step 2: Gradually Reduce Sodium Intake
Rather than making drastic changes, gradually reduce your sodium intake. Begin by cutting down on processed foods, which are often high in sodium. Opt for fresh ingredients and use herbs and spices to flavor your meals instead of salt.
Step 3: Increase Fruits and Vegetables
Aim to include fruits and vegetables in every meal. These foods are rich in potassium, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals. Strive for a variety of colors to ensure a wide range of nutrients.
Step 4: Choose Whole Grains
Replace refined grains with whole grains. Foods like whole wheat bread, brown rice, oatmeal, and quinoa are excellent sources of fiber and nutrients, contributing to better digestive health and sustained energy levels.
Step 5: Opt for Lean Proteins
Incorporate lean protein sources such as chicken, turkey, fish, beans, and legumes into your diet. These options are lower in saturated fat and provide essential amino acids for muscle maintenance and overall health.
Step 6: Include Low-Fat Dairy
Select low-fat or fat-free dairy products to meet your calcium needs without excessive saturated fat. Yogurt, milk, and cheese are good options, but be mindful of added sugars in some products.
Step 7: Healthy Fats in Moderation
While the DASH diet limits saturated fats, it encourages the consumption of healthy fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are beneficial for heart health when consumed in moderation.
Step 8: Plan and Prepare Meals
Planning and preparing meals in advance can help you stick to the DASH diet. Create a weekly meal plan, make a shopping list, and prepare meals at home to control ingredients and portion sizes effectively.
Sample DASH Diet Meal Plan
Day 1:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal topped with fresh berries and a sprinkle of nuts.
- Snack: A banana and a handful of almonds.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, and a light vinaigrette dressing.
- Snack: Carrot sticks with hummus.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli.
- Dessert: A small bowl of mixed fruit.
Day 2:
- Breakfast: Whole grain toast with avocado and a poached egg.
- Snack: Low-fat yogurt with a handful of granola.
- Lunch: Lentil soup with a side of mixed green salad.
- Snack: Sliced apple with a small amount of peanut butter.
- Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with brown rice and assorted vegetables.
- Dessert: A small serving of dark chocolate.
Day 3:
- Breakfast: Smoothie made with spinach, banana, and low-fat milk.
- Snack: Sliced cucumbers with low-fat cottage cheese.
- Lunch: Turkey and vegetable wrap with whole wheat tortilla.
- Snack: A handful of mixed nuts.
- Dinner: Grilled shrimp with whole wheat pasta and a side of asparagus.
- Dessert: Baked apple slices with cinnamon.
Tips for Success on the DASH Diet
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is crucial for overall health and helps manage hunger. Aim for at least 8 cups of water a day, and more if you are physically active.
Read Food Labels
Learn to read food labels to make informed choices. Look for products with low sodium, added sugars, and unhealthy fats. Opt for items with high fiber and protein content.
Mindful Eating
Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger and fullness cues. Avoid distractions during meals, such as watching TV or using electronic devices, to better enjoy and appreciate your food.
Regular Physical Activity
Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine to enhance the benefits of the DASH diet. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Seek Support
Having support from family, friends, or a dietitian can be beneficial in maintaining the DASH diet. Sharing your goals and progress with others can provide motivation and accountability.
Conclusion
The DASH diet offers a practical and sustainable approach to achieving optimal health. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, reducing sodium intake, and promoting overall wellness, the DASH diet can significantly improve heart health, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Implementing this diet requires mindful planning and dedication, but the long-term health benefits are well worth the effort.
FAQ’s
What is the DASH diet?
The DASH diet is a nutritional plan aimed at reducing blood pressure and promoting heart health by emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy.
What foods are recommended on the DASH diet?
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (like chicken, fish, and beans), low-fat dairy, and healthy fats (such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil).
How does the DASH diet lower blood pressure?
By reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium, calcium, and magnesium-rich foods, the DASH diet helps relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Can the DASH diet help with weight loss?
Yes, it promotes weight loss by encouraging whole, nutrient-dense foods and portion control.
Is the DASH diet suitable for people with diabetes?
Yes, it helps regulate blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity.
What are the sodium intake recommendations for the DASH diet?
2,300 mg per day for the standard diet, and 1,500 mg per day for the lower sodium version.
Can the DASH diet improve heart health?
Yes, it lowers blood pressure and LDL cholesterol, promoting cardiovascular health.
How can I start the DASH diet?
Assess your current diet, reduce sodium intake gradually, increase fruits and vegetables, choose whole grains, opt for lean proteins and low-fat dairy, and plan meals in advance.
What are some sample meals on the DASH diet?
Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries. Lunch: Grilled chicken salad. Dinner: Baked salmon with quinoa. Snacks: Fresh fruit and carrot sticks with hummus.
Can I follow the DASH diet if I am vegetarian or vegan?
Yes, by using plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, tofu, and nuts.
Are there any side effects of the DASH diet?
Generally safe, but some might experience changes in taste and digestion when transitioning.
Where can I find more information about the DASH diet?
Check resources from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), the American Heart Association (AHA), or consult healthcare providers.
Read more:
- Mediterranean Diet Plans: Health Benefits and Easy Recipes
- The 9 Best Diet Plans for Your Overall Health
- 10 Tips for Successful Weight loss
- A Comprehensive Guide of BMI
- Ultimate Guide to the Keto Diet: How to Lose Weight with Keto Diet
- Ricki Lake Weight loss : “You Won’t Believe How Ricki Lake Lost 30 Pounds!”
- Reduce Your Risk of Depression with These Tips
- Reduce Belly Fat with These Simple Home Workouts