Dive into this comprehensive guide to understanding BMI. Learn what BMI is, its importance, categories, limitations, and tips for maintaining a healthy BMI.
1.What is BMI?
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a figure obtained by dividing a person’s weight by their height squared. It’s a simple yet effective tool that helps determine whether an individual has a healthy body weight relative to their height. By assessing this ratio, healthcare professionals can identify potential weight-related health risks.
2.How BMI is Calculated
BMI is determined using this formula: BMI = weight (kg) / (height (m))^2. For instance, if someone weighs 70 kilograms and is 1.75 meters tall, their BMI would be calculated as follows:
BMI = 70 / (1.75)^2 = 22.9
The resulting number places them in a specific Body Mass Index category, which we’ll explore further.
You can easily calculate your BMI using online BMI Calculator.
3. The Importance of BMI
Health Implications of BMI
Maintaining a healthy BMI is paramount for overall well-being. A BMI outside the normal range can significantly increase the risk of various health conditions. These include heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain cancers. Moreover, individuals with an unhealthy BMI may experience reduced energy levels, decreased mobility, and a lower quality of life.
BMI and Overall Well-being
Achieving and sustaining a healthy BMI isn’t just about physical health—it’s also about mental and emotional well-being. When you’re at a healthy weight, you’re likely to feel more confident, energetic, and optimistic. This positivity can permeate various aspects of your life, from personal relationships to professional endeavors.
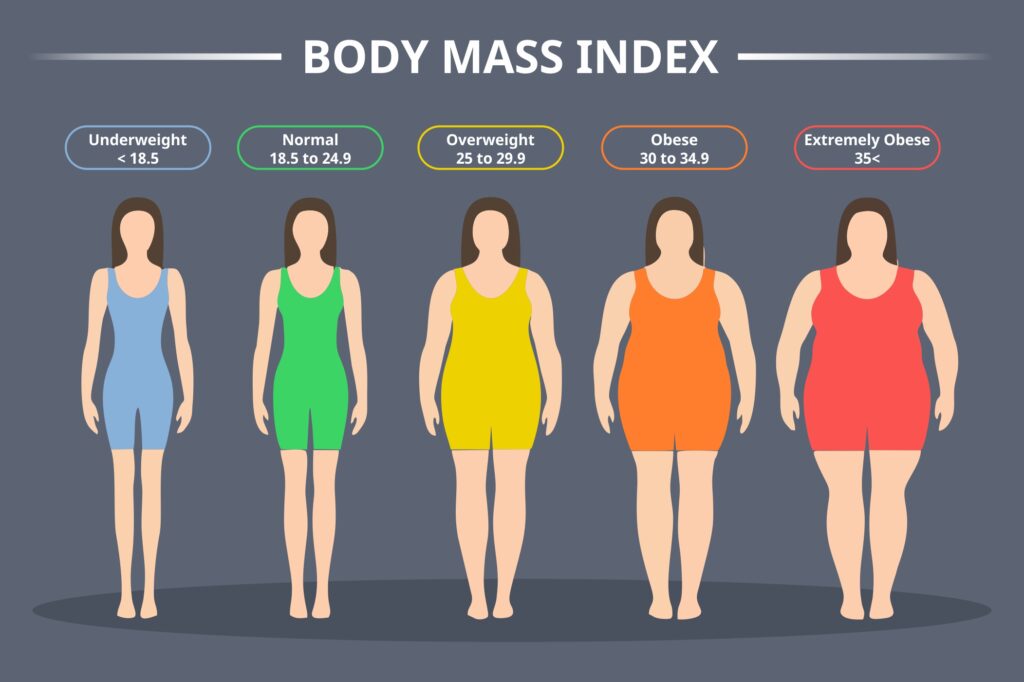
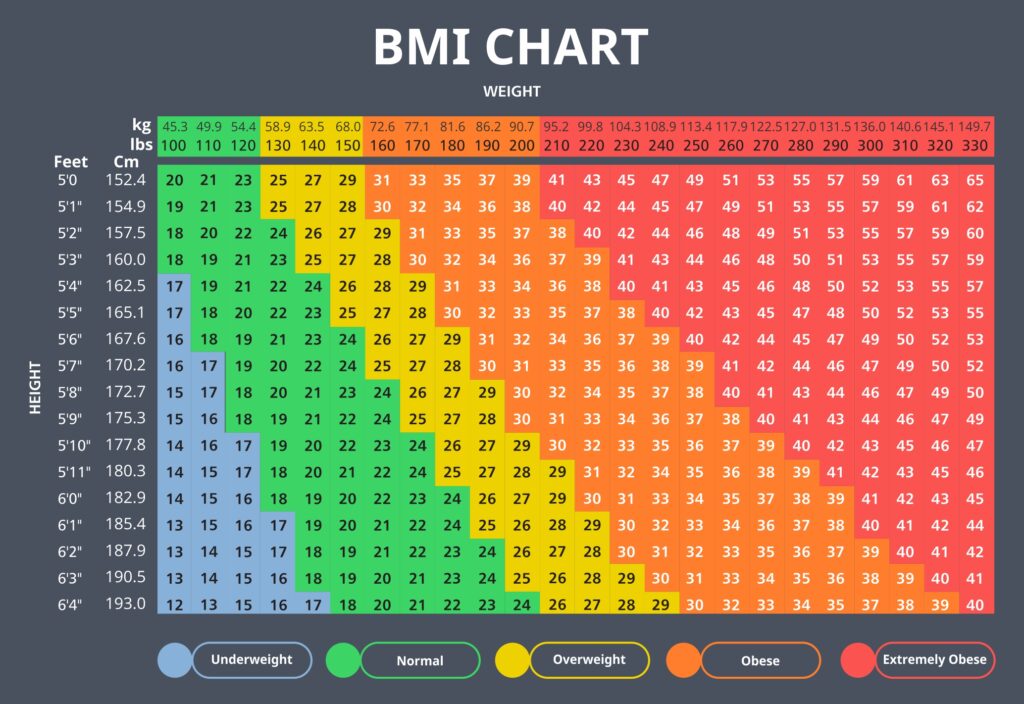
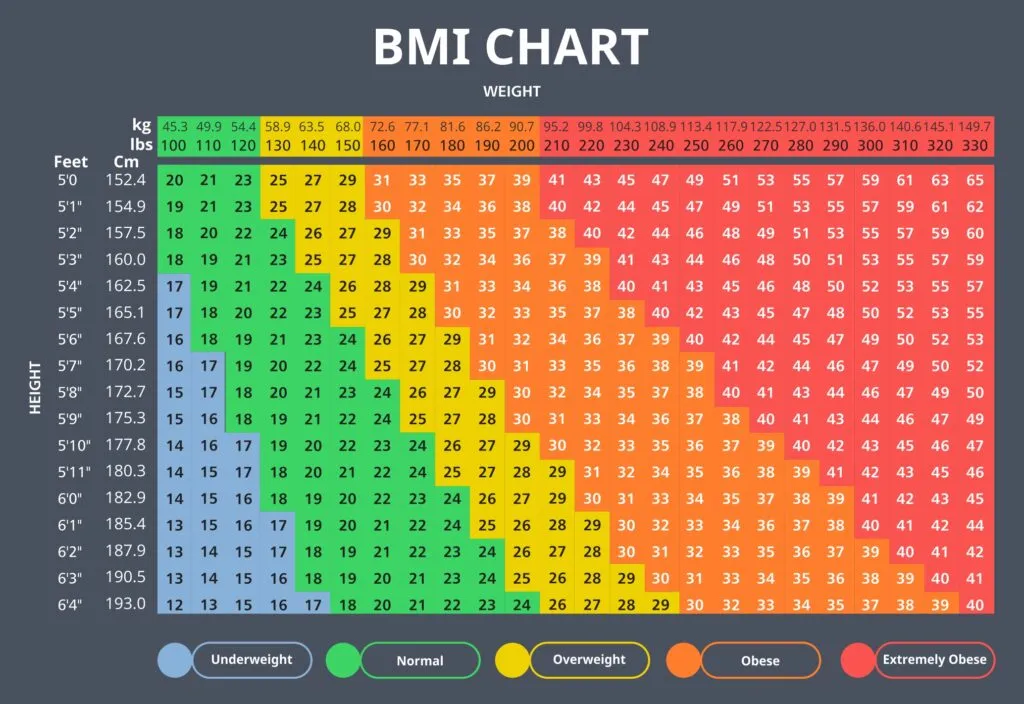
4. BMI Categories
Underweight
A BMI below 18.5 is categorized as underweight. Being underweight isn’t just a matter of aesthetics; it poses serious health risks. Individuals with a low BMI may have weakened immune systems, nutritional deficiencies, and an increased susceptibility to infections.
Normal Weight
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 falls within the normal weight range. This category is associated with the lowest risk of weight-related health problems. However, it’s essential to note that a “normal” BMI doesn’t necessarily equate to optimal health. Other factors like diet, exercise, and genetics also play crucial roles.
Overweight
A BMI between 25 and 29.9 indicates overweight status. Overweight individuals are at a higher risk of developing health issues, such as cardiovascular diseases, sleep apnea, and osteoarthritis.
Obesity
A BMI of 30 or above categorizes someone as obese. Obesity significantly elevates the risk of severe health conditions like coronary artery disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
5. Limitations of BMI
Muscle Mass vs. Fat Mass
A significant limitation of BMI is its inability to distinguish between muscle and fat mass. As a result, individuals with high muscle mass, like athletes or bodybuilders, may have a high BMI despite having low body fat percentages. Conversely, someone with low muscle mass may have a normal BMI but elevated body fat levels.
Ethnicity and BMI
BMI calculations may not be universally applicable across different ethnic groups. For example, people of Asian descent may have different body compositions compared to Caucasians or Africans. Thus, BMI readings should be interpreted with caution and in conjunction with other health assessments.
6. Maintaining a Healthy BMI
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining a healthy BMI. Focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Reduce your consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-calorie snacks to maintain a healthy BMI.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for achieving and sustaining a healthy BMI. Strive to participate in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercises weekly, like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Additionally, include strength training sessions in your routine at least twice a week to develop muscle mass and enhance metabolism.
7. Conclusion
BMI serves as a useful starting point for assessing weight status and identifying potential health risks. However, it’s essential to recognize its limitations and use it in conjunction with other health indicators. By prioritizing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and overall wellness, you can achieve and maintain a healthy BMI, leading to a happier, healthier life.
8. FAQs
Que : What is a healthy BMI range?
Ans : A healthy BMI usually ranges between 18.5 and 24.9.
Que : Can BMI be inaccurate?
Ans : Yes, BMI can be inaccurate for individuals with high muscle mass or different ethnic backgrounds.
Que : How often should I check my BMI?
Ans : It’s advisable to check your BMI annually or whenever you notice significant changes in your weight or health status.
Que : Can children’s BMI be calculated the same way as adults?
Ans : No, children’s BMI is calculated differently, taking into account their age and gender.
Que : Is BMI a good indicator of health?
Ans : While BMI provides valuable insights into weight status, it’s not a comprehensive indicator of overall health. Other factors such as diet, exercise, genetics, and lifestyle habits also influence health outcomes.
Que : How can I lower my BMI?
Ans : To lower your BMI, focus on adopting healthy eating habits, engaging in regular physical activity, and making sustainable lifestyle changes that promote weight loss.
Read more :