Introduction
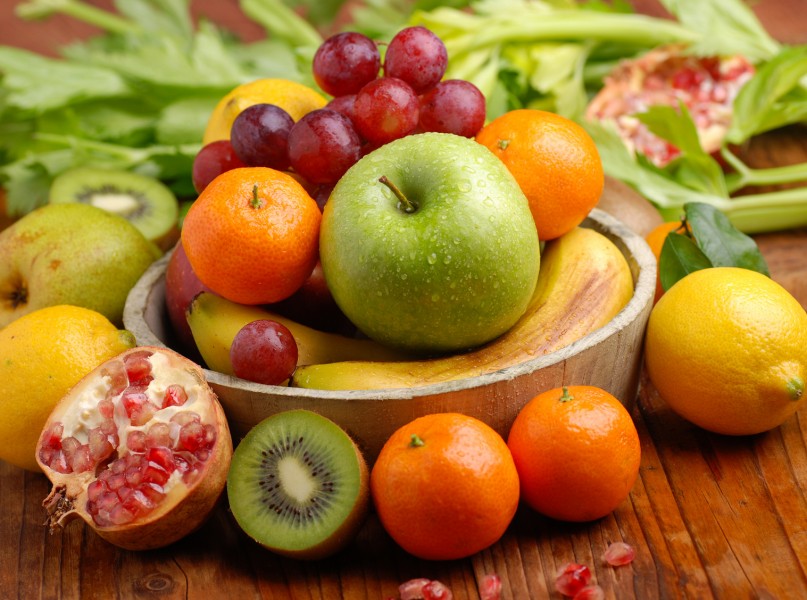
Eating more fruit may reduce your risk of depression, according to recent studies. The research highlights the importance of dietary patterns, specifically the intake of fruits, in lowering the likelihood of developing depression. Rich in antioxidants, dietary fiber, and vitamins, fruits can positively impact mental health by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and improving gut health. By incorporating a variety of fruits into your daily diet, you can take a significant step towards mitigating the risk of depression.
Relevance and Importance of the Study
Depression constitutes a significant public health quandary on a global scale. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 5 percent of the adult population worldwide endures depression, with approximately 280 million individuals afflicted by the condition. Depression is approximately 50 percent more prevalent among women than men, and over 75 percent of individuals in low-to-middle-income nations receive no treatment. The discovery of dietary influences on mental health provides a potentially accessible and cost-effective method for managing this pervasive condition.
Novel Research on Fruit Consumption and Risk of Depression
The novel research, spearheaded by Postdoctoral Fellow Annabel Matison from the University of New South Wales Sydney’s (UNSW) Centre for Healthy Brain Ageing (CHeBA), has for the inaugural time addressed a research lacuna pertaining to older adults aged 45 and above. “Compared with depression in younger cohorts, depression in older adults exerts a more pronounced impact on physical performance and cognition and is correlated with a diminished quality of life and elevated mortality rate,” Matison elucidated.
Study Objectives and Methodology
“Our objective with this investigation was to scrutinize the correlations between fruit and vegetable consumption and depression in individuals aged 45 years and older.” Participants in this study were drawn from diverse regions spanning six continents, including the United States, Sweden, Brazil, Nigeria, Malaysia, and Australia. The research, published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, assessed 7801 community-dwelling adults devoid of depression and unveiled a salutary association between heightened fruit consumption and a diminished risk of depression over a nine-year span.
Findings and Implications
“This intriguing discovery of a protective link between fruit consumption and the risk of depression underscores the necessity of accentuating diet in healthcare,” Matison remarked. Although the findings also hinted at a favorable relationship between vegetable consumption and a reduced risk of depression, it was not statistically significant, she added. “The rationale behind the beneficial link for fruit but not vegetable consumption might be that vegetables are typically ingested cooked, potentially affecting their nutrient composition, whereas fruit is usually consumed raw,” she expounded.
Nutritional Components and Mechanisms
The participants self-reported their fruit and vegetable intake through a detailed food frequency questionnaire, a concise food questionnaire, or diet history. Depressive symptoms were gauged using “validated measures,” the researchers noted, while the Cox regression method was employed to examine the relationships between consumption and depression over a follow-up duration of three to nine years.
Role of Nutrients in Mental Health
It has been postulated that the high levels of antioxidants, dietary fiber, and vitamins in fruits and vegetables may exert a positive influence on depression through various mechanisms, such as their roles in inflammation, oxidative stress, and the gut microbiota, the researchers observed. Given the distinct nutrient profiles of various fruits and vegetables, it also appears plausible that different types may exert differing impacts on the risk of depression. The study highlighted that the evidence for citrus fruits and green leafy vegetables being linked to a lower risk of depression is particularly compelling.
Future Research Directions
Professor Henry Brodaty, co-author and CHeBA co-director, asserted that future research focusing on the consumption of different types of fruits and vegetables—and concentrating on larger cohorts of older adults—is warranted, especially in low- and middle-income countries. “The extension of current research into the genetic factors associated with dietary intake offers a promising avenue to influence fruit and vegetable consumption,” Professor Brodaty stated. “We should also contemplate the varieties of fruits and vegetables consumed to better comprehend the interrelationships involved, and studies should be designed to provide more comparability across cohorts.”
Practical Implications for Diet and Health


Incorporating fruits into daily diet can be simple and enjoyable. Health experts recommend aiming for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables each day. Suggested fruit varieties for mental health benefits include berries, citrus fruits, apples, and bananas. Here are some tips for increasing fruit consumption:
- Add fruit to your breakfast cereal or yogurt.
- Keep fresh fruit available for snacks.
- Include fruit in your salads and main dishes.
- Try fruit-based desserts.
Expert Insights
Quotes from Annabel Matison and Henry Brodaty highlight the significant findings and potential future research directions. Additional insights from nutrition and mental health experts emphasize the importance of a balanced diet in mental health management.
Personal Stories or Case Studies
Real-life examples of individuals benefitting from increased fruit consumption can be powerful. Consider the story of Maria, a 50-year-old woman from Brazil, who experienced a significant improvement in her depressive symptoms after incorporating more fruits into her diet. Similar case studies from different regions can illustrate the global relevance of the research findings.
Preventive Measures
Dietary strategies to prevent depression include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Regular physical activity.
- Adequate sleep.
- Stress management techniques such as mindfulness and meditation. The role of an overall healthy lifestyle cannot be overstated in preventing mental health issues.
Conclusion
The study on fruit consumption and depression provides compelling evidence that a diet rich in fruits can significantly reduce the risk of depression, especially in older adults. By incorporating a variety of fruits into your daily diet, you can enjoy both the physical and mental health benefits they offer. Further research is needed to explore the genetic factors and the impact of different types of fruits and vegetables on mental health. This study underscores the necessity of accentuating diet in healthcare and the importance of making dietary changes to improve overall well-being.
FAQ’s
Que : What is the risk of depression?
Ans : The likelihood of developing depressive symptoms or being diagnosed with depression based on factors like genetics, environment, lifestyle, and diet.
Que : How does fruit consumption reduce the risk of depression?
Ans : Fruits contain antioxidants, dietary fiber, and vitamins that reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, and improve gut health, all of which help lower depression risk.
Que : What types of fruits are most effective in reducing depression risk?
Ans : Berries, citrus fruits, apples, and bananas are particularly beneficial due to their rich nutrient profiles.
Que : How much fruit should I consume to reduce my risk of depression?
Ans : Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables each day.
Que : Can vegetables also reduce the risk of depression?
Ans : Yes, but the study found a stronger link with fruits. The benefits may vary depending on whether vegetables are consumed raw or cooked.
Que : Are there other lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of depression?
Ans : Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques like mindfulness and meditation can also help reduce depression risk.
Que : What further research is needed on this topic?
Ans : Further research is needed to explore genetic factors and the impact of different types of fruits and vegetables on mental health in larger and more diverse populations.
Read more: